1. 우선순위 큐
1.1 우선순위 큐란?
큐(Queue)는 먼저 들어오는 데이터가 먼저 나가는 FIFO(First In First Out) 형식의 자료구조이다.
우선순위 큐(Priority Queue)는 먼저 들어오는 데이터가 아니라, 우선순위가 높은 데이터가 먼저 나가는 형태의 자료구조이다.
우선순위 큐는 일반적으로 힙(Heap)을 이용하여 구현한다.
1.2 힙이란?
힙(Heap)은 우선순위 큐를 위해 고안된 완전이진트리 형태의 자료구조이다.
여러 개의 값 중 최댓값 또는 최솟값을 찾아내는 연산이 빠르다.
힙의 특징
- 완전이진트리 형태로 이루어져 있다.
- 부모노드와 서브트리간 대소 관계가 성립된다. (반정렬 상태)
- 이진탐색트리(BST)와 달리 중복된 값이 허용된다.
힙의 종류
-
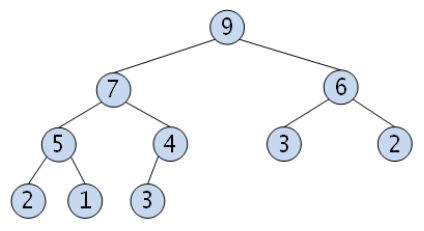
최대 힙 (Max Heap)
부모 노드의 키 값이 자식 노드보다 크거나 같은 완전이진트리이다.
❝ key(부모노드) ≥ key(자식노드) ❞
-
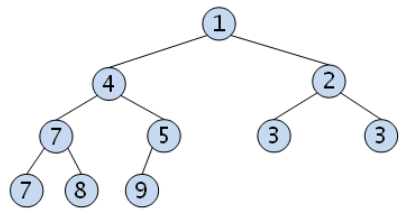
최소 힙 (Min Heap)
부모 노드의 키 값이 자식 노드보다 작거나 같은 완전이진트리이다.
❝ key(부모노드) ≥ key(자식노드) ❞
1.3 우선순위 큐 구현방법 비교
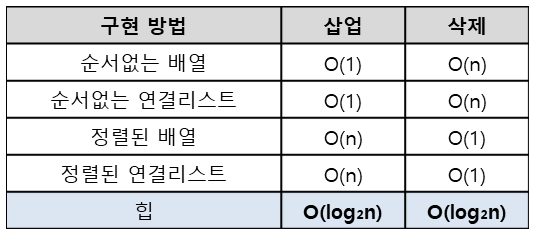
우선순위 큐를 힙이 아니라 배열 또는 연결리스트를 이용하여 구현할 수도 있다.
하지만 배열과 연결리스트는 선형 구조의 자료구조이므로 삽입 또는 삭제 연산을 위한 시간복잡도는 O(n)이다.
반면 힙트리는 완전이진트리 구조이므로 힙트리의 높이는 log₂(n+1)이며, 힙의 시간복잡도는 O(log₂n)이다.
아래는 이를 정리한 표이다.
1.4 우선순위 큐 ADT
객체
- 우선순위를 가진 요소들의 모음
연산
- insert(x) : 우선순위 큐에 요소 x 추가
- remove() : 우선순위 큐에서 가장 우선순위가 높은 요소를 삭제하고 반환
- find() : 우선순위 큐에서 가장 우선순위가 높은 요소를 반환
2. 우선순위 큐 구현
2.1 힙 구현
힙은 일반적으로 배열을 이용하여 구현한다.
완전 이진트리이므로 중간에 비어있는 요소가 없기 때문이다.
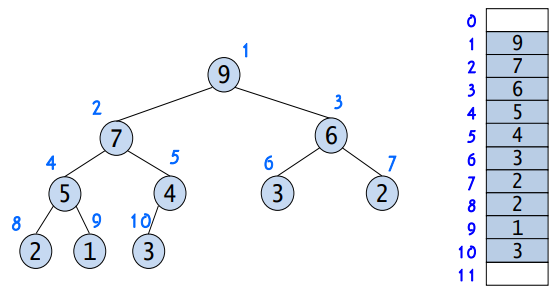
위 그림과 같이 트리의 각 노드에 번호를 붙이고, 이 번호를 배열의 인덱스로 생각하면 효과적으로 힙을 구현할 수 있다.
배열로 구현하였기 때문에 부모 또는 자식 노드를 찾아가는 연산을 구현하기도 간편하다.
자식노드를 구하고 싶을 때
- 왼쪽 자식노드 index = (부모 노드 index) * 2
- 오른쪽 자식노드 index = (부모 노드 index) * 2 + 1
부모노드를 구하고 싶을 때
- 부모 노드 index = (자식노드 index) / 2
2.2 삽입 연산
힙에 삽입을 하기 위해서는 힙 트리의 성질을 만족시키면서 새로운 요소를 추가해야 한다.
삽입 방법
- 우선 완전이진트리의 마지막 노드에 이어서 새로운 노드를 추가한다.
- 추가된 새로운 노드를 부모의 노드와 비교하여 교환한다.
- 정상적인 힙트리가 될 때 까지 (더이상 부모노드와 교환할 필요가 없을 때까지) 2번을 반복한다.
최악의 경우 새로 추가된 노드가 루트노트까지 비교하며 올라가야 하므로 시간복잡도가 O(log₂n)이다.
2.3 삭제 연산
힙 트리에서 루트노드가 가장 우선순위가 높으므로 루트 노드를 삭제해야 한다.
삭제가 이뤄진 후 힙 트리의 성질이 유지돼야 하므로 아래와 같은 방법으로 삭제를 진행한다.
삭제 방법
- 루트 노드를 삭제한다.
- 루트 노드가 삭제된 빈자리에 완전이진트리의 마지막 노드를 가져온다.
- 루트 자리에 위치한 새로운 노드를 자식 노드와 비교하여 교환한다.
이때 최대 힙인 경우 자식노드 중 더 큰 값과 교환을 하며, 최소 힙인 경우 더 작은 값과 교환을 한다. - 정상적인 힙트리가 될 때까지 (더 이상 자식노드와 교환할 필요가 없을 때까지) 3번을 반복한다.
삭제 연산 또한 최악의 경우 루트노트부터 가장 아래까지 내려가야 하므로 시간복잡도가 O(log₂n)이다.
2.4 우선순위 큐 구현 (C++)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_ELEMENT 200 // heap array size
template <typename T>
struct Node{
private:
int key;
T data;
public:
Node(){
key = 0;
}
Node(int _key, T _data){
key = _key;
data = _data;
}
~Node(){}
// getter/setter
int getKey(){
return key;
}
void setKey(int _key){
key = _key;
}
T getData(){
return data;
}
void setData(T _data){
data = _data;
}
};
template <typename T>
class MaxHeap{
private:
Node<T> node[MAX_ELEMENT];
int size; // heap 요소 개수
public:
MaxHeap(){
size = 0;
}
~MaxHeap(){}
// search node
Node<T>& getParent(int index){
return node[index/2];
}
Node<T>& getLeftChild(int index){
return node[index*2];
}
Node<T>& getRightChild(int index){
return node[index*2+1];
}
// 삽입
void insert(int key, T data){
if(isFull()){
cout << "Heap is Full" << endl;
return;
}
int index = ++size; // 힙트리 마지막 노드의 다음 위치에서 시작
// 힙트리를 거슬러 올라가며 부모 노드와 비교
while(index != 1 && key > getParent(index).getKey()){
node[index] = getParent(index);
index /= 2;
}
// 최종 위치에 데이터 삽입
node[index].setKey(key);
node[index].setData(data);
}
// 삭제
T remove(){
if(isEmpty()){
cout << "Heap is Empty" << endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
Node<T> itemNode = node[1]; // root node (삭제 대상)
Node<T> lastNode = node[size--]; // 힙트리의 마지막 노드
int index = 1; // 마지막 노드의 index (root 부터 시작)
// root 부터 내려가며 자식 노드와 비교
while(index <= size){
if(index*2 > size){ // leaf node인 경우 (자식 노드가 없는 경우)
break;
}else if(index*2 == size){ // 자식노드가 하나인 경우
if(lastNode.getKey() < getLeftChild(index).getKey()){
node[index] = getLeftChild(index);
index *= 2;
}else{
break;
}
}else{ // 자식노드가 두개인 경우
int leftChildKey = getLeftChild(index).getKey();
int rightChildKey = getRightChild(index).getKey();
// 둘 중 key가 더 큰 자식노드와 교환
if(lastNode.getKey() < leftChildKey || lastNode.getKey() < rightChildKey){
node[index] = leftChildKey > rightChildKey ? getLeftChild(index) : getRightChild(index);
index = leftChildKey > rightChildKey ? index*2 : index*2+1;
}else{
break;
}
}
}
node[index] = lastNode; // 마지막 노드를 최종 위치에 저장
return itemNode.getData(); // 삭제 노드의 data 반환
}
// 출력
void display(){
int level = 1;
for(int i=1; i<= size; i++){
if(i == level){
cout << endl;
level *= 2;
}
cout << node[i].getData() << "(" << node[i].getKey() << ") ";
}
cout << '\n' << "-------------------------" << endl;
}
bool isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
bool isFull(){
return size == MAX_ELEMENT - 1;
}
};
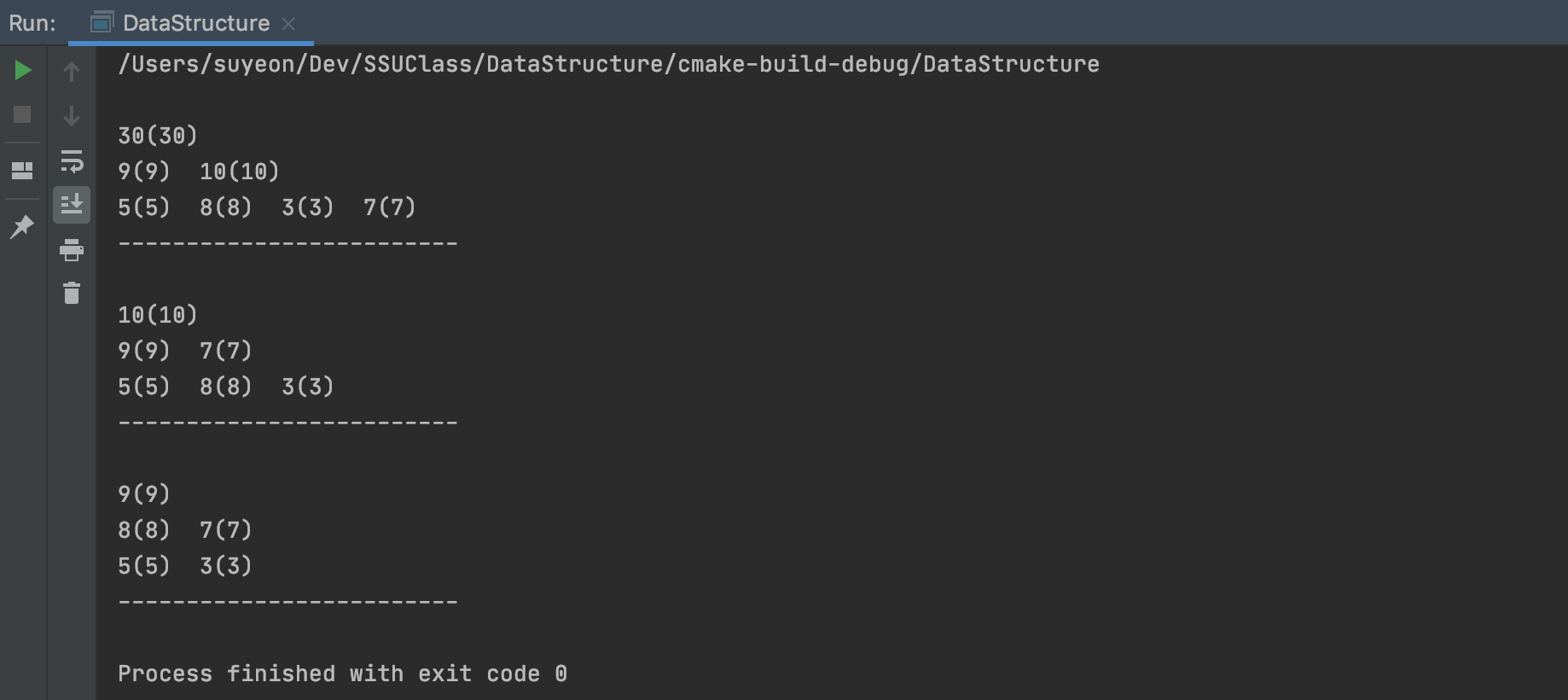
int main(){
MaxHeap<int> priorityQueue;
// 삽입
priorityQueue.insert(10, 10);
priorityQueue.insert(5, 5);
priorityQueue.insert(30, 30);
priorityQueue.insert(8, 8);
priorityQueue.insert(9, 9);
priorityQueue.insert(3, 3);
priorityQueue.insert(7, 7);
priorityQueue.display();
// 삭제
priorityQueue.remove();
priorityQueue.display();
priorityQueue.remove();
priorityQueue.display();
return 0;
}
2.5 C++에서의 우선순위 큐 사용 (STL)
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
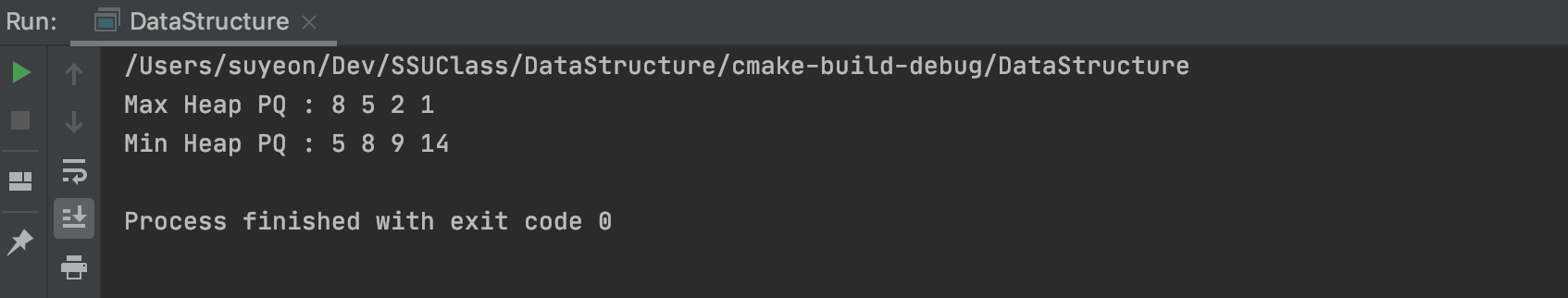
int main(){
// Max Heap
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, less<int>> pq1;
pq1.push(5);
pq1.push(2);
pq1.push(8);
pq1.push(9);
pq1.push(1);
pq1.push(14);
pq1.pop();
pq1.pop();
cout << "Max Heap PQ : ";
while(!pq1.empty()){
cout << pq1.top() << " ";
pq1.pop();
}
cout << endl;
// Min Heap
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> pq2;
pq2.push(5);
pq2.push(2);
pq2.push(8);
pq2.push(9);
pq2.push(1);
pq2.push(14);
pq2.pop();
pq2.pop();
cout << "Min Heap PQ : ";
while(!pq2.empty()){
cout << pq2.top() << " ";
pq2.pop();
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
2.6 [응용] 힙 정렬 (Heap Sort)
힙 정렬이란 최대 힙트리나 최소 힙트리를 이용한 정렬 알고리즘 중 하나이다.
힙 정렬 알고리즘
- n개의 요소를 하나씩 힙에 삽입한다.
- n번에 걸쳐 힙에서 요소를 하나씩 삭제하고 반환된 값을 순차적으로 정렬한다.
앞에서 힙의 삽입·삭제 시간복잡도는 O(log₂n) 이라는 것을 알아보았다.
힙 정렬을 위해 n번의 삽입과 n번의 삭제가 이뤄지므로 정렬에 필요한 전체 시간은 log₂n + log₂n에 비례한다.
이는 O(log₂n) 시간복잡도로 표현 가능하며, 삽입정렬과 같은 간단한 정렬 알고리즘의 시간복잡도가 O(n²)이라는 것과 비교했을 때 매우 효율적인 알고리즘이다.
특히 힙 정렬은 전체 자료를 정렬하는 것보다 전체에서 가장 큰 값 몇 개가 필요할 때 유용하다.
C++ 힙 정렬 구현
/*
* 8.5
* Max Heap을 이용하여 내림차순 힙 정렬 구현
*/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_ELEMENT 200 // heap array size
struct Node{
private:
int key;
public:
Node(){
key = 0;
}
Node(int _key){
key = _key;
}
~Node(){}
// getter/setter
int getKey(){
return key;
}
void setKey(int _key){
key = _key;
}
};
class MaxHeap{
private:
Node node[MAX_ELEMENT];
int size; // heap 요소 개수
public:
MaxHeap(){
size = 0;
}
~MaxHeap(){}
// search node
Node& getParent(int index){
return node[index/2];
}
Node& getLeftChild(int index){
return node[index*2];
}
Node& getRightChild(int index){
return node[index*2+1];
}
// 삽입
void insert(int key){
if(isFull()){
cout << "Heap is Full" << endl;
return;
}
int index = ++size; // 힙트리 마지막 노드의 다음 위치에서 시작
// 힙트리를 거슬러 올라가며 부모 노드와 비교
while(index != 1 && key > getParent(index).getKey()){
node[index] = getParent(index);
index /= 2;
}
// 최종 위치에 데이터 삽입
node[index].setKey(key);
}
// 삭제
int remove(){
if(isEmpty()){
cout << "Heap is Empty" << endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
Node itemNode = node[1]; // root node (삭제 대상)
Node lastNode = node[size--]; // 힙트리의 마지막 노드
int index = 1; // 마지막 노드의 index (root 부터 시작)
// root 부터 내려가며 자식 노드와 비교
while(index <= size){
if(index*2 > size){ // leaf node인 경우 (자식 노드가 없는 경우)
break;
}else if(index*2 == size){ // 자식노드가 하나인 경우
if(lastNode.getKey() < getLeftChild(index).getKey()){
node[index] = getLeftChild(index);
index *= 2;
}else{
break;
}
}else{ // 자식노드가 두개인 경우
int leftChildKey = getLeftChild(index).getKey();
int rightChildKey = getRightChild(index).getKey();
// 둘 중 key가 더 큰 자식노드와 교환
if(lastNode.getKey() < leftChildKey || lastNode.getKey() < rightChildKey){
node[index] = leftChildKey > rightChildKey ? getLeftChild(index) : getRightChild(index);
index = leftChildKey > rightChildKey ? index*2 : index*2+1;
}else{
break;
}
}
}
node[index] = lastNode; // 마지막 노드를 최종 위치에 저장
return itemNode.getKey(); // 삭제 노드의 data 반환
}
bool isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
bool isFull(){
return size == MAX_ELEMENT - 1;
}
};
// 힙 정렬
void heapSort(int a[], int n){
MaxHeap heap;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
heap.insert(a[i]);
}
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
a[i] = heap.remove();
}
}
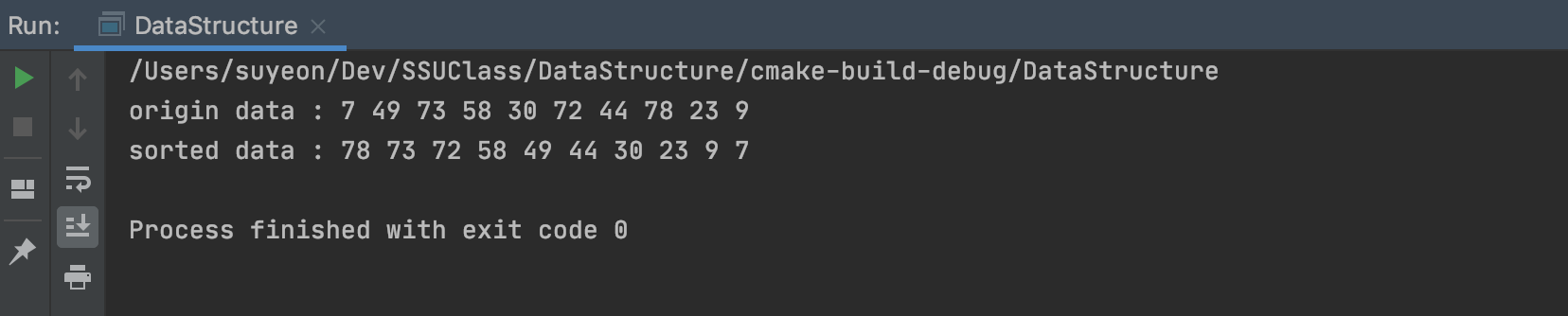
int main(){
int data[10];
for(int i=0; i<10; i++){
data[i] = rand() % 100; // random data
}
cout << "origin data : ";
for(int i=0; i<10; i++) cout << data[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
heapSort(data, sizeof(data)/sizeof(int));
cout << "sorted data : ";
for(int i=0; i<10; i++) cout << data[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
오름차순 구현을 위해서는 Min Heap을 사용하고, 내림차순 구현을 위해서는 Max Heap을 사용하는 것이 편하다.
![[자료구조] 우선순위 큐와 힙 (Priority Queue & Heap)](https://img1.daumcdn.net/thumb/R750x0/?scode=mtistory2&fname=https%3A%2F%2Fblog.kakaocdn.net%2Fdn%2FcT2Dxb%2FbtqSATggBLA%2FCIBeKSLq0s6MDTNVM345Jk%2Fimg.png)